What is ClassLoader in Java
ClassLoader in Java is a class that is used to load class files in Java. Java code is compiled into a class file by javac compiler and JVM executes Java program, by executing byte codes written in the class file. ClassLoader is responsible for loading class files from file systems, networks, or any other source.
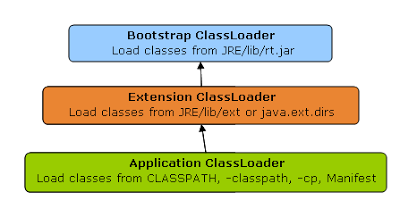
There is three default class loader used in Java, Bootstrap, Extension, and System or Application class loader.
Every class loader has a predefined location, from where they load class files. The bootstrap class loader is responsible for loading standard JDK class files from rt.jar and it is the parent of all class loaders in Java.
The bootstrap class loader doesn't have any parents if you call String.class.getClassLoader() it will return null and any code based on that may throw NullPointerException in Java. The bootstrap class loader is also known as Primordial ClassLoader in Java.
Extension ClassLoader delegates class loading request to its parent, Bootstrap, and if unsuccessful, loads class form jre/lib/ext directory or any other directory pointed by java.ext.dirs system property. Extension ClassLoader in JVM is implemented by sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader.
The third default class loader used by JVM to load Java classes is called System or Application class loader and it is responsible for loading application specific classes from CLASSPATH environment variable, -classpath or -cp command line option, Class-Path attribute of Manifest file inside JAR.
Application class loader is a child of Extension ClassLoader and its implemented by sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader class. Also, except for the Bootstrap class loader, which is implemented in the native language mostly in C, all Java class loaders are implemented using java.lang.ClassLoader.
In short here is the location from which Bootstrap, Extension, and Application ClassLoader load Class files.
1) Bootstrap ClassLoader - JRE/lib/rt.jar
2) Extension ClassLoader - JRE/lib/ext or any directory denoted by java.ext.dirs
3) Application ClassLoader - CLASSPATH environment variable, -classpath or -cp option, Class-Path attribute of Manifest inside JAR file.
How ClassLoader works in Java?
What is ClassLoader in Java, How classloader works in JavaAs I explained earlier Java ClassLoader works in three principles: delegation, visibility, and uniqueness. In this section, we will see those rules in detail and understand the working of Java ClassLoader with example. By the way here is a diagram that explains How ClassLoader to load class in Java using delegation.
How ClassLoader works in Java?
What is ClassLoader in Java, How classloader works in JavaAs I explained earlier Java ClassLoader works in three principles: delegation, visibility, and uniqueness. In this section, we will see those rules in detail and understand the working of Java ClassLoader with example. By the way here is a diagram that explains How ClassLoader to load class in Java using delegation.

1. Delegation principles
As discussed on when a class is loaded and initialized in Java, a class is loaded in Java, when it's needed. Suppose you have an application-specific class called Abc.class, the first request of loading this class will come to Application ClassLoader which will delegate to its parent Extension ClassLoader which further delegates to Primordial or Bootstrap class loader.
Primordial will look for that class in rt.jar and since that class is not there, a request comes to Extension class loader which looks on jre/lib/ext directory and tries to locate this class there, if the class is found there than Extension class loader will load that class and Application class loader will never load that class but if it's not loaded by extension class-loader than Application class loader loads it from Classpath in Java. Remember Classpath is used to load class files while PATH is used to locate executables like javac or java command.
2. Visibility Principle
According to the visibility principle, Child ClassLoader can see class loaded by Parent ClassLoader but vice-versa is not true. This means if class Abc is loaded by Application class loader than trying to load class ABC explicitly using extension ClassLoader will throw either java.lang.ClassNotFoundException. as shown in the below Example
package test;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* Java program to demonstrate How ClassLoader works in Java,
* in particular about the visibility principle of ClassLoader.
*
* @author Javin Paul
*/
public class ClassLoaderTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
//printing ClassLoader of this class
System.out.println("ClassLoaderTest.getClass().getClassLoader() : "
+ ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader());
//trying to explicitly load this class again using Extension class loader
Class.forName("test.ClassLoaderTest", true
, ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader().getParent());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(ClassLoaderTest.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
}
Output:
ClassLoaderTest.getClass().getClassLoader() : sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@601bb1
16/08/2012 2:43:48 AM test.ClassLoaderTest main
SEVERE: null
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: test.ClassLoaderTest
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:202)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:190)
at sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader.findClass(Launcher.java:229)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:306)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:247)
at java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method)
at java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:247)
at test.ClassLoaderTest.main(ClassLoaderTest.java:29)
3. Uniqueness Principle
According to this principle, a class loaded by Parent should not be loaded by Child ClassLoader again. Though it's completely possible to write a class loader which violates Delegation and Uniqueness principles and loads class by itself, it's not something which is beneficial. You should follow all class loader principles while writing your own ClassLoader.
How to load class explicitly in Java
Java provides API to explicitly load a class by Class.forName(classname) and Class.forName(classname, initialized, classloader), remember JDBC code which is used to load JDBC drives we have seen in Java program to Connect Oracle database.
As shown in the above example you can pass the name of ClassLoader which should be used to load that particular class along with the binary name of the class. Class is loaded by calling loadClass() method of java.lang.ClassLoader class which calls findClass() method to locate bytecodes for the corresponding class.
In this example, Extension ClassLoader uses java.net.URLClassLoader which searches for class files and resources in JAR and directories. any search path which is ended using "/" is considered a directory.
If findClass() does not found the class than it throws java.lang.ClassNotFoundException and if it finds it calls defineClass() to convert bytecodes into a .class instance which is returned to the caller.
Where to use ClassLoader in Java?
ClassLoader in Java is a powerful concept and used in many places. One of the popular examples of ClassLoader is AppletClassLoader which is used to load a class by Applet since Applets are mostly loaded from the internet rather than a local file system.
By using separate ClassLoader you can also load the same class from multiple sources and they will be treated as different classes in JVM. J2EE uses multiple class loaders to load a class from a different location like classes from the WAR file will be loaded by Web-app ClassLoader while classes bundled in EJB-JAR is loaded by another classloader.
Some web server also supports hot deploy functionality which is implemented using ClassLoader. You can also use ClassLoader to load classes from a database or any other persistent store.
That's all about What is ClassLoader in Java and How ClassLoader works in Java. We have seen delegation, visibility, and uniqueness principles which is quite important to debug or troubleshoot any ClassLoader related issues in Java. In summary knowledge of How ClassLoader works in Java is a must for any Java developer or architect to design Java application and packaging.