Implementing Angular route is a five step process: -
Step 1: Add the Angular-route.js file to your view.
<script src="~/Scripts/angular-route.js"></script>
Step 2: Inject ngroute functionality while creating Angular app object.
var app = angular.module("myApp", ['ngRoute']);Step 3: Configure the route provider.
In route provider, we need to define which URL pattern will load which view. For instance in the below code, we are saying Home loads Yoursite/Home view and Search loads YourSite/Search view.
app.config(['$routeProvider',
function ($routeProvider) {;
$routeProvider.
when('/Home, {
templateUrl: 'Yoursite/Home',
controller: 'HomeController'
}).
when('/Search', {
templateUrl: YourSite/Search',
controller: 'SearchController'
}).
otherwise({
redirectTo: '/'
});
}]);Step 4: Define hyperlinks.
Define hyper link with the # structure as shown below. So now when user clicks on the below anchor hyperlinks, these actions are forwarded to route provider and router provider loads the view accordingly.
<div>
<a href="#/Home">Home</a><br />
<a href="#/Search"> Search </a><br />
</div>
Step 5: Define sections where to load the view.
Once the action comes to the router provider, it needs a place holder to load views. That’s defined by using the ng-view tag on a HTML element. You can see in the below code we have created a DIV tag with a place holder. So the view will load in this section.
<div ng-view>
</div>
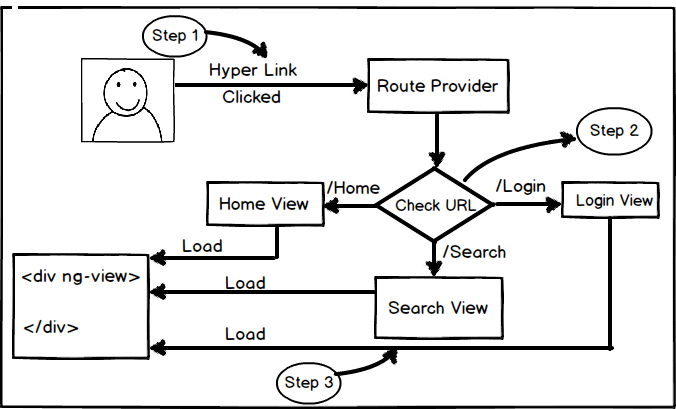
So if we summarize angular routing is a three step process (Below is a visual diagram for the same): -
- Step 1: End user clicks on a hyperlink or button and generates action.
- Step 2: This action is routed to the route provider.
- Step 3: Router provider scans the URL and loads the view in the place holder defined by
ng-view attribute.